What is the boa constrictor?
The boa constrictor, also known as Boa constrictor, is a non-venomous snake native to the Americas. It belongs to the Boidae family, the same as anacondas, and its main hunting characteristic is how it wraps its body around prey and slowly crushes them until they suffocate.
It has no venom, which debunks one of the biggest myths surrounding these animals. Its imposing appearance and slow movements contribute to its reputation as a silent and majestic predator.
In Brazil, the boa can be found almost nationwide, from the tropical forests of the Amazon to the cerrado and caatinga. It is a wildlife species protected by law, meaning its possession and breeding must follow specific environmental regulations.
Boa species and types worldwide and in Brazil
Although the name "boa" generally refers to Boa constrictor, this species has several subspecies distributed across different regions of the Americas. Below are some of the most well-known:
🌍 Worldwide:
- Boa constrictor constrictor: found in South America, including Brazil.
- Boa constrictor imperator: common in Central America, especially in Mexico and Honduras.
- Boa constrictor occidentalis: native to Argentina and Paraguay, endangered.
- Boa constrictor amarali: also present in Brazil, particularly in the cerrado.
🇧🇷 In Brazil:
- Common boa (Boa constrictor constrictor): the most well-known and widespread across the country.
- Caatinga boa (Boa constrictor amarali): adapted to the semi-arid climate, with a paler coloration and smaller size.
Each subspecies has unique color patterns and sizes, fascinating researchers, wildlife photographers, and herpetology enthusiasts. The boa is undoubtedly a silent star of Brazilian fauna!
Nicknames of the boa constrictor
The boa, scientifically known as Boa constrictor, goes by various popular names across Brazil. Besides boa constrictor and red-tailed boa, it's also called deer snake or salamanta in some regions. In the Amazon, names like araramboia, araboia, green boa, parrot snake, and periquitamboia are common. In Tupi, its original name is mboi or mboia, which simply means "snake."
Surprising facts about the boa constrictor
Have you heard that snakes swallow whole cows? Well, that's a baseless popular myth, but when it comes to the boa, some truths are even more impressive:
- It's not venomous, but extremely effective: the boa kills its prey by constriction, squeezing them until respiratory collapse.
- Its eyes are adapted to darkness: even in low light, it can see with precision.
- It senses the prey's heat: thanks to thermal sensors on its head, it accurately identifies mammals and birds.
- It plays a vital role in nature: controls rodent populations and maintains ecological balance.
- It can live up to 30 years: especially in monitored environments like zoos or rehabilitation centers.
- It swallows prey whole: due to its extremely flexible jaw, it can ingest whole animals, even those with skulls larger than its head.
These traits make the Boa Constrictor one of the most incredible reptiles in South American wildlife, and knowing these details helps dispel the unfounded fear many people have.
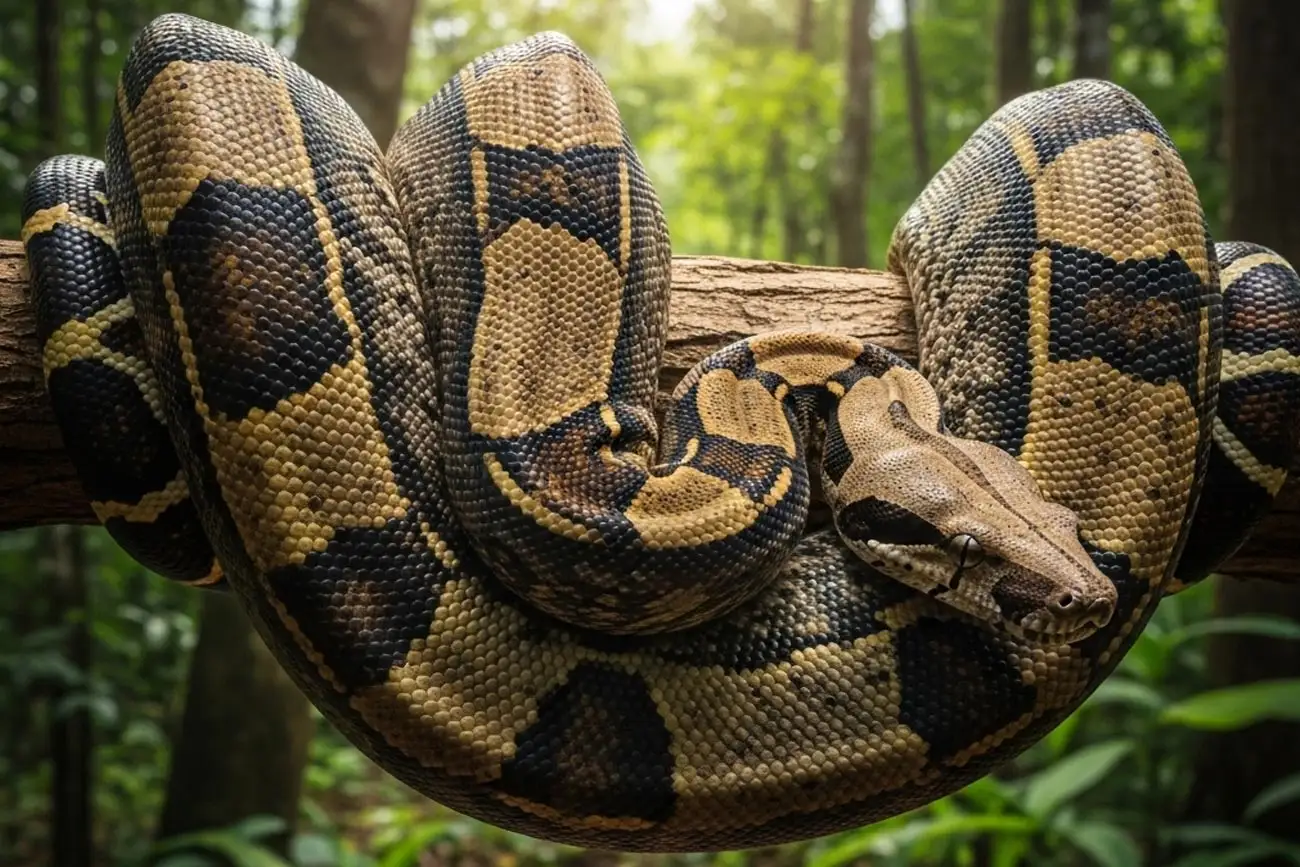

Why is the boa so special?
The Boa Constrictor is essential for ecosystem balance. As a mid-level predator in the food chain, it helps control populations of rodents, birds, and small mammals. This prevents ecological imbalance and even reduces urban pests.
Additionally, its exotic beauty and calm behavior (yes, it doesn’t attack humans spontaneously!) fascinate researchers, conservationists, and the curious. The boa is often studied in biodiversity projects due to its resilience and adaptation to various habitats.
Did you know many indigenous communities see the boa as a symbol of wisdom and protection? This cultural relationship reveals how it’s present not just in the physical environment but also in popular imagination.
Can it be kept in captivity?
This is one of the most common—and controversial—questions. The Boa Constrictor is a wildlife species protected by law in Brazil. Therefore, domestic breeding is only allowed with IBAMA authorization and from licensed breeders.
It's important to note that it is not considered an exotic pet but rather a native wildlife species with great ecological value. Thus:
- Capturing boas from the wild is prohibited.
- Acquisition should only be from authorized breeders.
- Documentation and microchipping are mandatory.
In other words, before considering keeping a boa at home, it's essential to understand its complexity and remember its primary role is in nature.
Moreover, keeping a boa in captivity requires:
- An enclosure with controlled temperature and humidity.
- Feeding with appropriate rodents, live or pre-killed.
- Knowledge about the snake's behavior and health.
- Legal registration with environmental agencies.
Conclusion? The boa can live in captivity but should never be treated as a "common pet." Its care demands responsibility, respect, and love for nature.
Conservation challenges and how to help
Unfortunately, even as one of the most adaptable species, the Boa Constrictor faces growing threats:
- Deforestation and habitat destruction
- Illegal hunting for the pet trade
- Deaths due to fear and prejudice
Many people still kill boas out of fear, which is unfounded. Unlike venomous snakes, the boa is peaceful, shy, and avoids human contact whenever possible.
What you can do to help:
- Educate others about the boa's role in the ecosystem.
- Report wildlife trafficking.
- Support wildlife conservation NGOs.
- Avoid buying animals without legal documentation.
- Share informative content like this.
Protecting the boa means protecting nature as a whole.
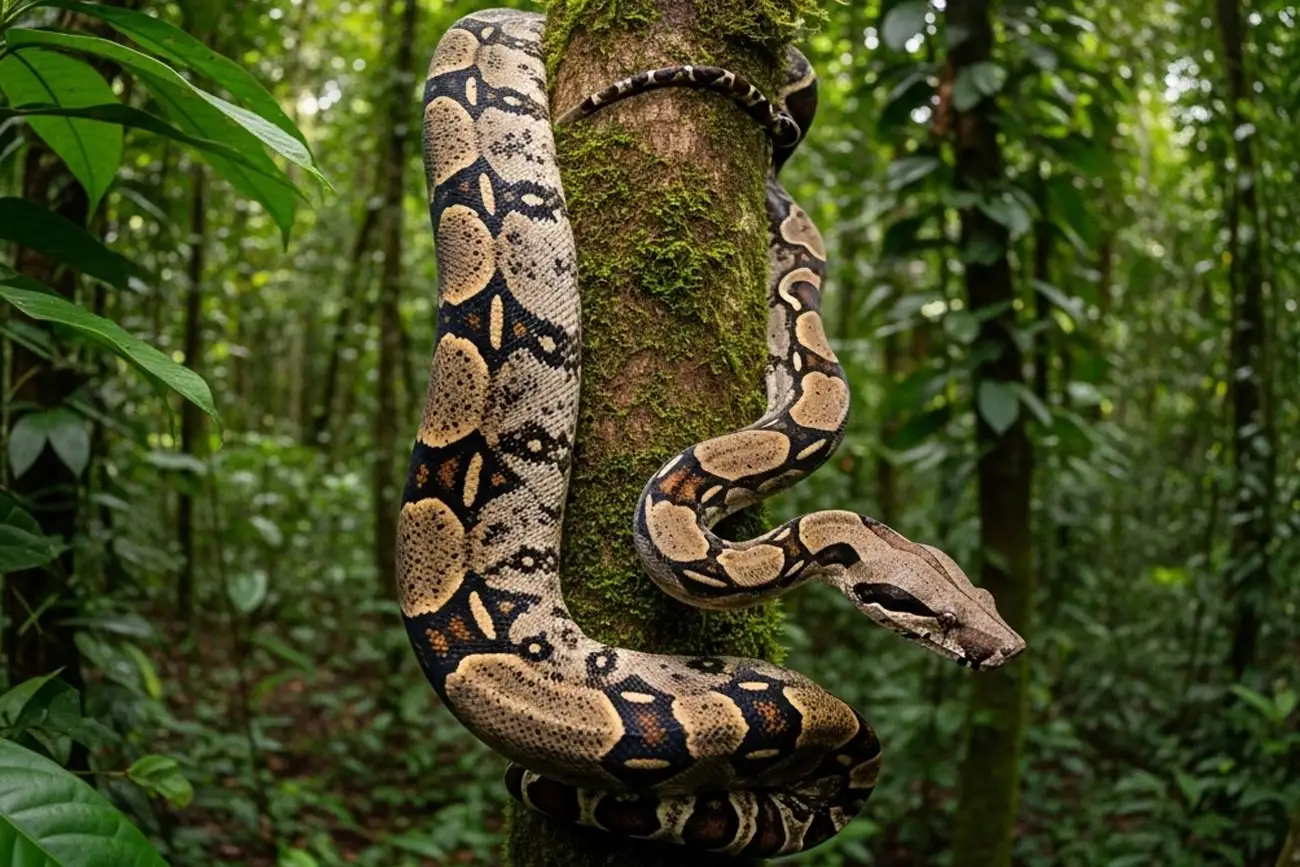

Tips for nature and wildlife lovers
If you're passionate about animals and want to connect with nature responsibly, here are some suggestions:
- Visit ethical rehabilitation centers and zoos.
- Watch documentaries about Brazilian wildlife.
- Join wildlife observation projects.
- Read books and follow biologists and conservationists.
- Avoid myths: not all snakes are dangerous!
The boa is a symbol of Brazilian biodiversity. By valuing it, we promote a more respectful relationship with the environment.
The boa deserves respect and admiration!
Throughout this article, you've learned that the Boa Constrictor is much more than a mysterious serpent. It is a pillar of ecosystems, a marvel of evolution, and a living being that deserves our respect and protection.
Share this content with your friends and help spread knowledge about these incredible animals. Let’s combat fear with information and prejudice with empathy!
👉 Want to learn more about wildlife and Brazilian fauna curiosities? Keep exploring Adore Pets' blog and don’t forget to follow our social media!















Add comment