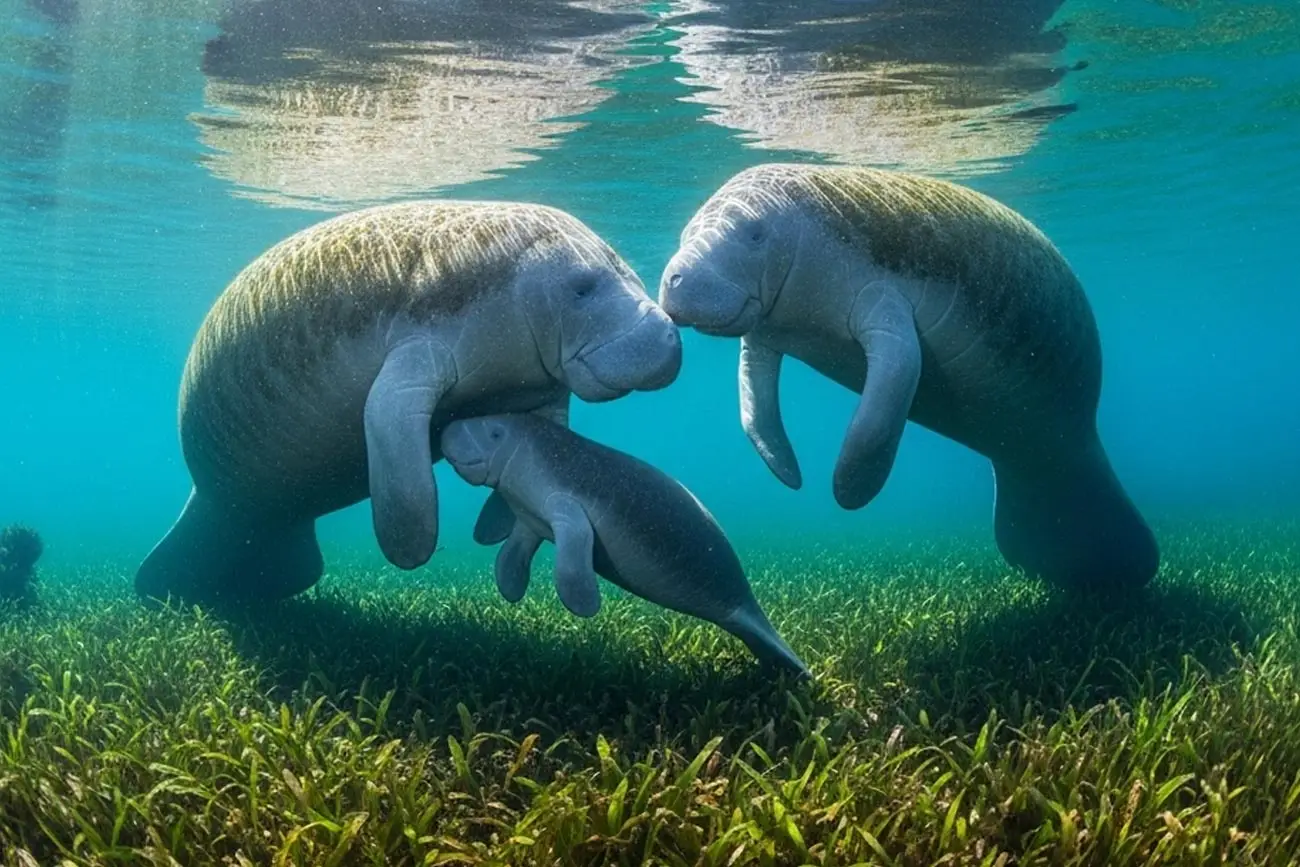
What is the manatee?
The Manatee, scientifically known as Trichechus inunguis (in the Amazon) and Trichechus manatus (on the Atlantic coast), is a herbivorous aquatic mammal that inhabits rivers, estuaries, and tropical coastal areas. Despite its name, it is not a fish, but a close relative of elephants and hippos!
- Physical characteristics: robust body, no flattened tail like other sirenians; paddle-shaped front flippers; thick and wrinkled skin.
- Diet: feeds almost exclusively on aquatic plants, consuming up to 10% of its body weight daily!
- Habitat: found in three main populations in Brazil: Amazonian manatee (rivers of the Amazon basin), northern coastal marine manatee, and eastern coastal marine manatee.
Its lifespan can exceed 60 years, making it one of the longest-lived aquatic mammals. However, this longevity is no guarantee of survival, as their reproduction rates are low: a female gives birth to only one calf every two or three years on average.
Surprising facts about the manatee
- Adaptable nostrils: the nostrils close tightly when the animal dives, preventing water from entering.
- Tactile sensitivity: the skin on the snout is covered with highly sensitive vibrissae (whiskers) that help detect plants and obstacles in murky waters.
- "Gentle heart": despite its size, the Manatee is known for its curiosity and patience around boats and humans. In many sanctuaries, it approaches visitors without fear!
- Thermal adaptation: lacking a dense blubber layer like whales, it seeks warmer areas during cold periods, migrating to shallow, protected waters.
- Ancestral connection: fossil records indicate its ancestors appeared over 40 million years ago, serving as a link between ancient and modern marine mammals.
Did you know it was so incredible? These facts show how unique the Manatee is—but also how each peculiarity makes it vulnerable to environmental changes.
Why is it so special?
Ecological impact
- Habitat engineer: while grazing, the Manatee helps maintain open channels in dense vegetation, benefiting fish and crustaceans.
- Nutrient recycling: by eating large amounts of plants, it contributes to nutrient cycles in aquatic ecosystems.
Cultural and touristic value
- Regions like the Jacuí Delta (RS) and Amazon rivers attract ecotourists seeking to observe these gentle giants.
- Riverside communities have incorporated the manatee into their legends and local crafts, strengthening regional identities and generating income through responsible wildlife tourism.
Emotional bonds
Have you ever felt that joy when seeing a majestic animal up close? The Manatee evokes immediate fascination: its serenity invites contemplation and connection with nature. For those who love exotic pets, the idea of interacting with a sirenian may be tempting—but it's crucial to remember that they cannot be kept as domestic pets. Their value lies in seeing them free!

Conservation challenges and how to help
Main threats
- Habitat loss: mangrove deforestation and river flow alterations reduce feeding and resting areas.
- Boat accidents: collisions with boats are a leading cause of death, as their thick skin and fragile bones make recovery from trauma difficult.
- Pollution: oil spills, plastic waste, and pesticides contaminate waters, harming the animals' health.
- Illegal hunting and trafficking: though prohibited, some populations still face persecution for their meat or trade.
Successful initiatives
- Sanctuaries and rehabilitation centers: places like the Manatee Project (AP) and the Aquatic Mammal Center (CE) rescue orphaned calves, rehabilitate, and release them back into the wild.
- GPS monitoring: satellite collars track migration routes and identify critical protection areas.
- Environmental education: workshops in schools and riverside communities raise awareness about sustainable practices.
How you can help
- Symbolically adopt a Manatee: many projects offer sponsorship certificates, with funds supporting conservation efforts.
- Avoid products impacting mangroves: choose certified wood and reduce pesticide use.
- Practice conscious tourism: when observing manatees, choose operators following minimum distance and silence protocols.
- Share knowledge: post facts and curiosities on social media to encourage more people to engage.
You can make a difference right now!
Visit the Viva o Peixe-Boi Brasil Project website to discover how to sponsor a calf or donate to sanctuary maintenance.
Tips for lovers of exotic pets and aquatic mammals
Although the Manatee is not a domestic pet, those fascinated by exotic animals can:
- Visit aquariums and environmental education centers with interactive tanks and responsible encounter programs.
- Specialize in aquatic biology or veterinary medicine to work with mammal rescue and rehabilitation.
- Support NGOs focused on wildlife by volunteering in wetland cleanups and rescued animal care.
- Engage in nature-connected hobbies like wildlife photography, mangrove kayaking, and scientific diving (with proper permits).
Additionally, for those considering a unique first pet, explore legal and suitable options like small aquatic turtles, axolotls, or ornamental fish—species that thrive in domestic captivity with proper care.
Understand that...
The Manatee is far more than a gentle giant: it is a symbol of resilience for Brazil's aquatic ecosystems. Each fact, each threat, and each conservation effort reveals how deeply it's intertwined with river and mangrove health—and our own quality of life.
Now it's your turn! Share this article on social media, comment on what surprised you most, and explore more Adore Pets content to keep learning about the incredible world of animals. Together, we can turn curiosity into action and ensure a brighter future for the majestic Manatee! 🐋💚















Add comment